 Azure VM with Azure Database
Azure VM with Azure Database
Install Kestra on Azure VM with Azure Database as a database backend and Blob Storage as internal storage backend.
This guide provides instructions for deploying Kestra on Azure VM with Azure Database as a database backend and Blob Storage as internal storage backend.
Prerequisites:
- basic knowledge about using a command line interface
- basic knowledge about Azure and PostgreSQL.
Create an Azure VM
First, create a virtual machine using Azure Virtual Machines. To do so, go to the Azure portal and choose Virtual Machines.
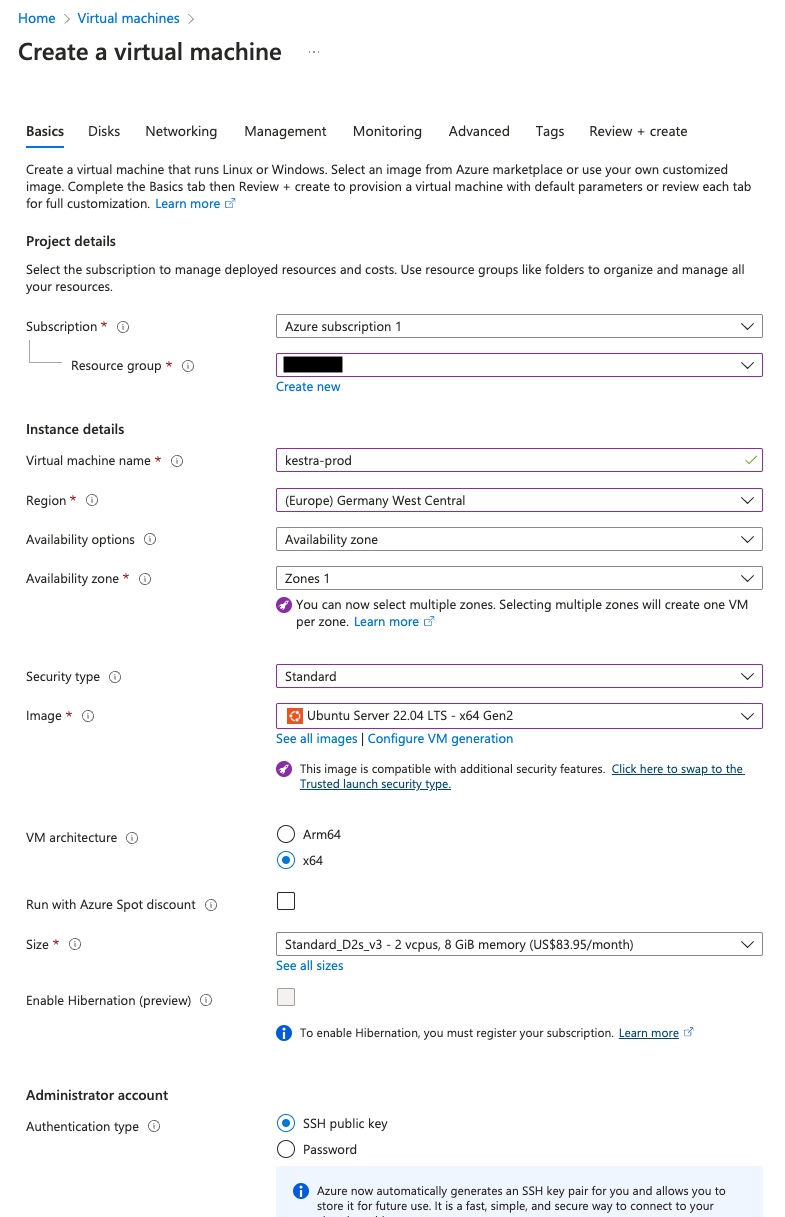
- Click on
Createand selectAzure Virtual Machine. - Choose an appropriate
SubscriptionandResource Group. - Give a name for your VM, and choose a
Regionwhere it should be launched. - For
Availability options, chooseAvailabilty zone, and keep the default availability zone. - For
Image, chooseUbuntu Server 22.04 LTS - x64 Gen2, andx64as the VM architecture. - Kestra needs at least 4GiB Memory and 2vCPU to run correctly. Choosing the
SizeasStandard_D2s_v3is a good starting point. - Select
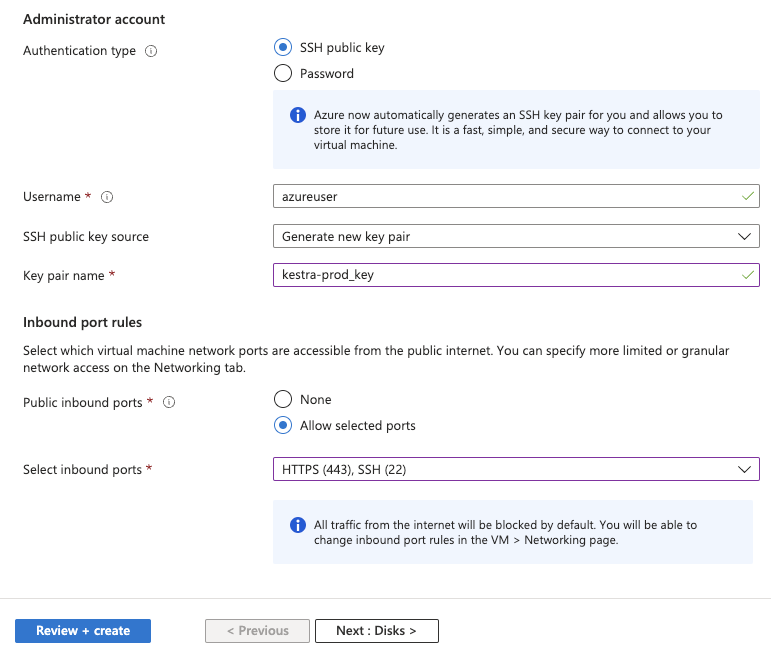
SSH public keyas theAuthentication type. - You can keep the default
azureuseras theUsername. - For
SSH public key source, you can selectGenerate new key pair, and provide an appropriate name for the key pair. - For
Public inbound ports, chooseAllow selected ports, and from theSelect inbound portsdropdown, selectHTTPSandSSH. - Click on
Review + Create. - You can now review the configurations and click on "Create". On the
Generate new key pairpopup, click onDownload private key and createresource.

Wait until the virtual machine is up and running.
Install Docker
In your terminal, run the following commands to SSH into the virtual machine:
chmod 400 <your-key-pair.pem>
ssh -i <your-key-pair.pem> azureuser@<your-VM-public-IP>
Kestra can be started directly from a .jar binary or using Docker. We’ll use Docker here for a quick setup:
- Install Docker on the Azure VM instance. You can find the last updated instruction on the Docker website.
- Install docker-compose.
To check your installation, run sudo docker version and sudo docker compose version. You're now ready to download and launch the Kestra server.
Install Kestra
Download the official Docker-Compose file:
curl -o docker-compose.yml \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kestra-io/kestra/develop/docker-compose.yml
Use an editor such as Vim to modify the docker-compose.yml, set basic authentication to true, and configure your basic authentication credentials to secure your Kestra instance.
kestra:
server:
basic-auth:
enabled: true
username: admin@kestra.io # it must be a valid email address
password: kestra
Then, use the following command to start the Kestra server:
sudo docker compose up -d
Allow external traffic
Kestra is now running and the Kestra server exposes traffic on the 8080 port. To connect through your web browser, update the inbound traffic rules in the Azure security group.
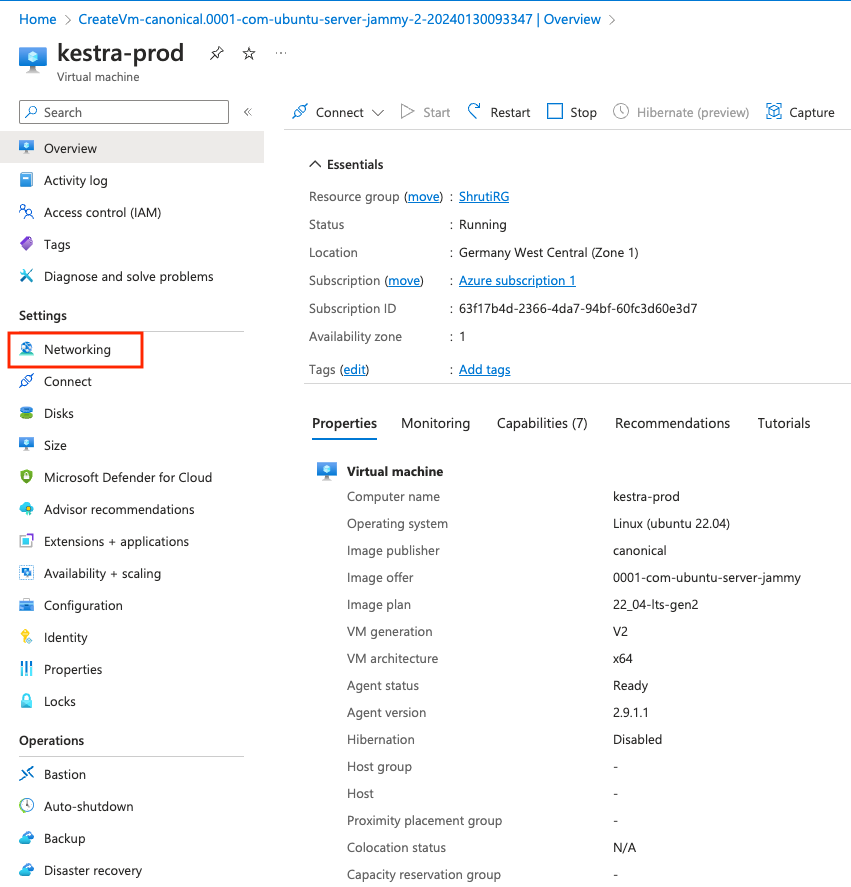
- Go to the Virtual Machines console, and select the recently created virtual machine.
- On the left navigation menu, click on
Networking. - Under
Inbound port rulestab, click on theAdd inbound port rulebutton. - In the
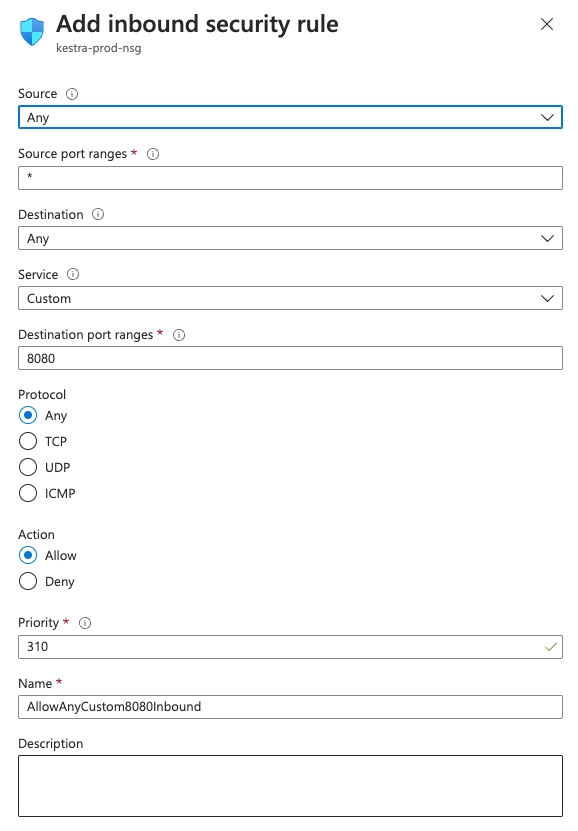
Add inbound security rulepage, putDestination port rangesas8080. You can keep the default values for the remaining properties. Finally, click onAddat the bottom of the page.
If you want to only allow traffic coming from your local machine, set the Source to your own IP address. To open the instance to the entire Internet, leave it at Any.
Note that if you haven't set up basic authentication in the previous step, your Kestra instance will be publicly available to anyone without any access restriction.
You can now access your Kestra instance and start developing flows.
Launch Azure Database
This first installation relies on a PostgreSQL database running alongside the Kestra server - on the VM instance (see the PostgreSQL service running thanks to the docker-compose).
For a simple proof of concept (PoC), you can keep the PostgreSQL database running in Docker.
However, for a production-grade installation, we recommend a managed database service such as Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers.
Launch a database using Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers
- Go to the Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers.
- Click on
Create Azure Database for PostgreSQL server(Kestra also supports MySQL, but PostgreSQL is recommended). - Choose an appropriate
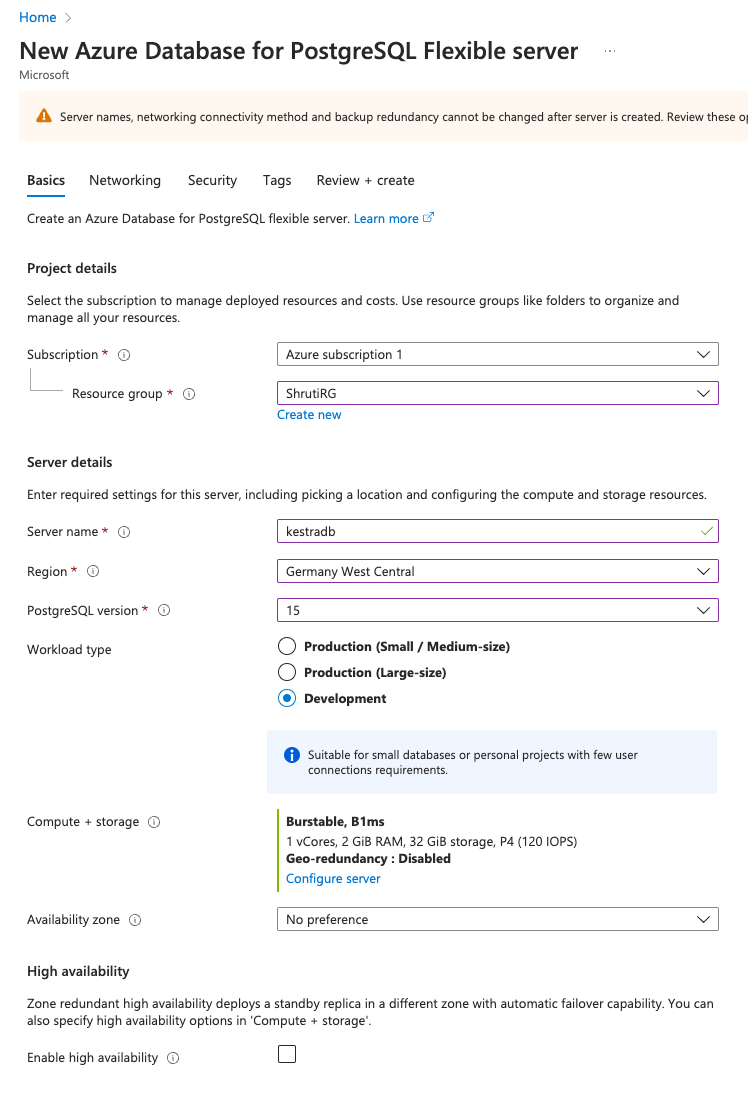
SubscriptionandResource Group. - Put an appropriate
Server name, and select the preferredRegion. - Choose the latest
PostgreSQL version. We recommend version 15. - Select the
Workload typeas per your requirement. - Choose
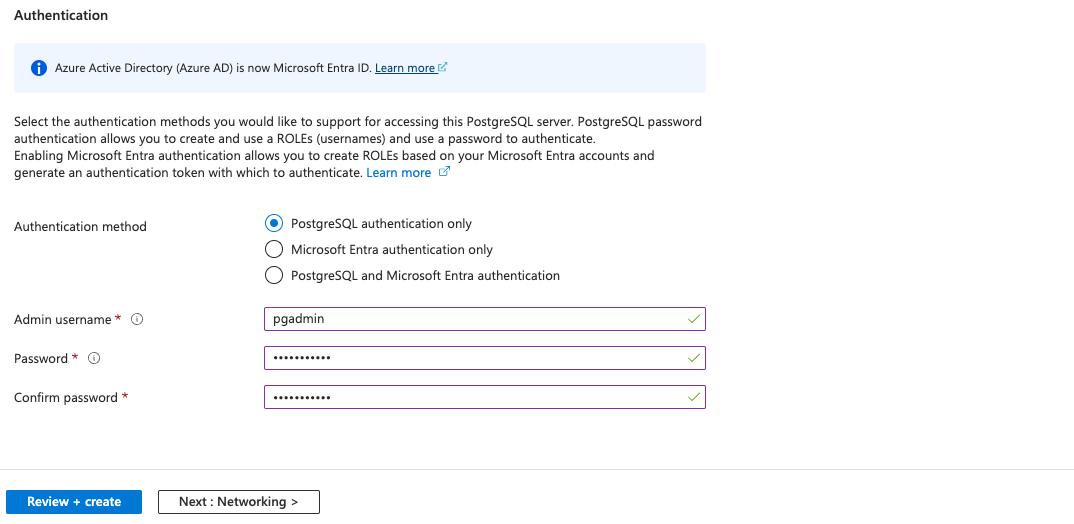
Authentication methodasPostgreSQL authentication only. - Provide an appropriate
Admin usernameandPassword, and re-write the password inConfirm password. - Click on
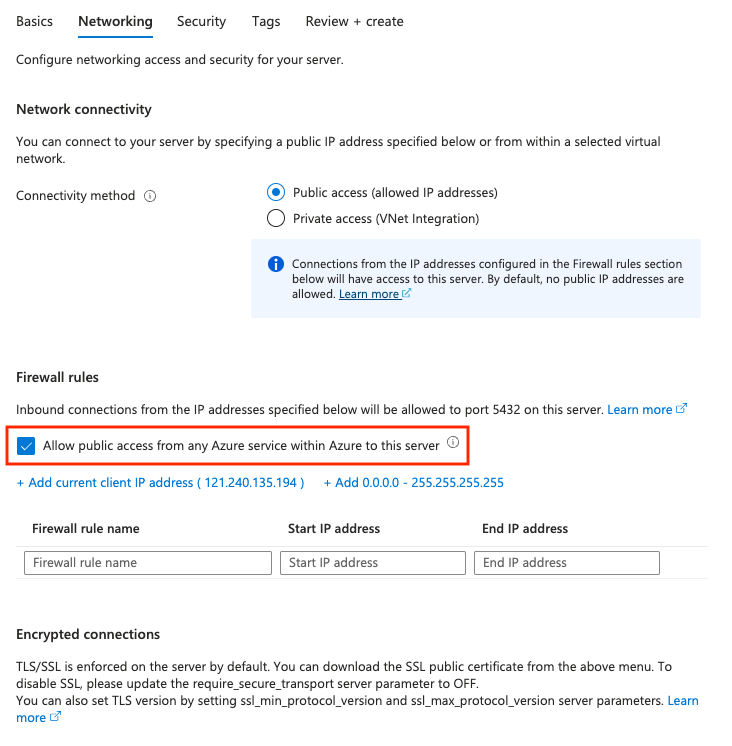
Next: Networking. - Click on the select box for
Allow public access from any Azure service within Azure to this server. - Click on
Review + Create. Review the configurations and click onCreate. - Wait for the database to be provisioned.
Create a Kestra database
- Go to the database overview page, and click on
Databasesfrom the left side navigation menu. - Click on
Add. - Put an appropriate database name, and click on
Saveat the top.
Update Kestra configuration
In the docker-compose configuration, edit the datasources property of the Kestra service to point Kestra to your Azure database:
datasources:
postgres:
url: jdbc:postgresql://<your-db-external-endpoint>:5432/<db_name>
driverClassName: org.postgresql.Driver
username: <your-username>
password: <your-password>
Because you now use the "Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers" service, you don't need the Postgres Docker service anymore. Remove it from the docker-compose.yml file.
In order for the changes to take effect, restart the docker services with sudo docker compose restart or sudo docker compose up -d.
Configure Azure Blob Storage
By default, internal storage is implemented using the local file system. This section will guide you on how to change the storage backend to Blob Storage to ensure more reliable, durable, and scalable storage.
- Go to the Storage Accounts.
- Click on
Create. - Choose an appropriate
SubscriptionandResource Group. - Put an appropriate
Storage account name, and select the preferredRegion. - Select
PerformanceandRedundancyas per your requirement. - Click on
Review, and post reviewing the configurations, click onCreate. - Click on the newly created storage account.
- On the storage account overview page, click on the
Containersfrom the left side navigation menu. - Click on
Createbutton at the top to create a new container. - Put an appropriate name for the container, and click on
Create. A new container will be created. - Now, click on
Access keysfrom the left side navigation menu. - For one of the keys, either key1 or key2, click on
Showfor theConnection string, and click onCopy to clipboardbutton. - Note down the connection string with you. We will require this for configuring the storage backend.
- Edit the Kestra storage configuration in the
docker-compose.ymlfile.
kestra:
storage:
type: azure
azure:
container: "<your-container>"
endpoint: "https://<your-storage-account>.blob.core.windows.net/"
connectionString: "<your-connection-string>"
In order for the changes to take effect, restart the docker services with sudo docker compose restart or sudo docker compose up -d.
For more information on Azure Blob storage configuration, check out the guide here.
Next steps
This guide walked you through installing Kestra on a Azure Virtual Machine with Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers and Azure Blob Storage as storage backend.
This setup provides a simple starting point for running Kestra in production on a single machine. For a deployment to a distributed Kubernetes cluster, check the Azure AKS deployment guide.
Reach out via Slack if you encounter any issues or if you have any questions regarding deploying Kestra to production.
Make sure to also check the CI/CD guide to automate your workflow deployments based on changes in Git.
Was this page helpful?